
08
Feb
The Science of Kidney and Dialysis
Excessive junk food causes kidney failure in later life due to our modern lifestyle and consumption compared with fewer natural and more artificial foods. It's also prevalent in people who have already been admitted to the hospital, especially those who are very ill and require intensive care.
When your kidneys stop filtering waste items from your blood, you have kidney failure. In such a case, hazardous levels of waste can build up, and your blood's chemical makeup can become unbalanced.
Kidneys and their function:
The kidneys are bodily organs that filter waste from the bloodstream. They also help regulate blood pressure, electrolyte balance, and red blood cell formation in the body.
They are found in the back of the abdomen, on either side of the spine. They receive blood directly from the aorta via the renal arteries and return blood to the heart via the renal veins to the vena cava.
Here are some major functions of the kidneys:
When your kidneys stop filtering waste items from your blood, you have kidney failure. In such a case, hazardous levels of waste can build up, and your blood's chemical makeup can become unbalanced.
Kidneys and their function:
The kidneys are bodily organs that filter waste from the bloodstream. They also help regulate blood pressure, electrolyte balance, and red blood cell formation in the body.
They are found in the back of the abdomen, on either side of the spine. They receive blood directly from the aorta via the renal arteries and return blood to the heart via the renal veins to the vena cava.
Here are some major functions of the kidneys:
- When blood travels to the kidney, sensors in specific kidney cells control how much water and electrolytes are excreted in the urine.
- Erythropoietin, a hormone that stimulates the creation of red blood cells in the bone marrow, is also produced by the kidneys.
- Special cells in the kidney keep track of the amount of oxygen in the blood.
- Each kidney produces urine, which travels through the ureter, a tube that links the kidney to the bladder.
Signs of kidney failure:
Kidney failure may not cause any symptoms at first (asymptomatic). The inability to control water and electrolyte balances, eliminate waste items from the body, and encourage red blood cell production are all symptoms that occur as kidney function declines.
The following kidney failure symptoms, if unnoticed or mistreated, can lead to life-threatening situations:
- Lethargy
- Weakness
- Breathing problems
- Swelling that is widespread (edema)
- Anaemia causes generalised weakness
- Appetite loss
- Fatigue
- Heart failure due to cardiomyopathy
- Potassium deficiency (hyperkalemia)
What is dialysis, and how does it help?
When the kidneys aren't working properly, waste builds up in the bloodstream. This can lead to a coma or perhaps death. Dialysis is used to treat people who have a serious kidney problem, such as severe kidney damage or past renal failure. It's needed when the kidneys have lost 90% of their function, and the glomerular filtration rate is less than 15. Because most kidney failures are irreparable, this treatment may be continued for months or years.
In such cases, dialysis is used to help the patient recover. Dialysis aids in the maintenance of bodily balance by performing the following tasks:
- It keeps your blood pressure in check.
- It removes excess water and metabolic waste from the body.
- Prevents hazardous amounts of potassium, bicarbonate, and sodium from accumulating in the body.
Healthy ways to overcome negativity through your Dialysis journey:
Going through dialysis might be a challenging journey for anyone. We have come up with a few tips and tricks that can help you overcome any medical anxiety. While you're at the centre, consider what other activities you'd like to undertake during your dialysis sessions.
Dialysis treatments might provide you with blocks of "me time" that you may not have previously had. Your treatment time is a terrific time to get caught up on things you've been meaning to accomplish or simply relax. If you're looking for a social outlet, ask your social worker or in-centre dialysis nurse if your centre offers any organised events.
Play some music: This is one of the most effective methods for unwinding during your treatment. In fact, research found that dialysis patients who listened to music experienced less pain and nausea than those who did not.
Write about your experience in a blog, a notebook, or a tweet: Writing can help you work through your emotions and provide you the opportunity to share your experiences with friends, family, or even new dialysis patients.
Mentor new dialysis patients: It can be really rewarding to assist someone who is new to dialysis therapy. Inquire with your social worker about volunteering at the centre or starting a mentoring programme.
Discover something new: Is there something you've always wanted to learn more about but never had the time? Dive right in. Take an online class, read a book, listen to a podcast, view a video, or take a podcast.
Be an expert on kidneys: Continue to learn everything you can about treatment choices. Remember that some people change the type of dialysis they use at some point, so knowing as much as possible is beneficial.
Going through an illness can be difficult and can have a negative impact on one's mental health, so one should always try to nourish their inner peace and do things that make them happy and satisfied. Positivity and mental strength are the best ways to get through any illness, and one should never give up hope.
Protocols of dialysis:
Dialysis is based on the ultrafiltration of fluid across a semipermeable membrane, as well as the concept of solute dissipation. Diffusion is a property of materials in water that causes them to move in the opposite direction of a concentration gradient.
Dialysate or separate dialysis fluids flow on one flank of the semipermeable screen, while blood flows on the other. A selectively permeable layer is a thin material membrane with pores or holes of various sizes.
Minor solutes and fluids pass through the layer, but larger substances are blocked by the membrane (large proteins, red blood cells). When blood flows into the kidneys, the larger compounds are separated from the minor ones in the glomerulus, simulating the filtering process that occurs in the kidneys.
On the other hand, dialysis should not be viewed as a permanent solution; rather, it should be viewed as a temporary substitute for the kidney's function until the kidney can repair itself. On the other hand, chronic renal damage seldom heals on its own, necessitating a kidney transplant. Patients who have a kidney transplant have a higher life expectancy than those who receive dialysis.
Types of dialysis:
There are two major types of dialysis:
Going through dialysis might be a challenging journey for anyone. We have come up with a few tips and tricks that can help you overcome any medical anxiety. While you're at the centre, consider what other activities you'd like to undertake during your dialysis sessions.
Dialysis treatments might provide you with blocks of "me time" that you may not have previously had. Your treatment time is a terrific time to get caught up on things you've been meaning to accomplish or simply relax. If you're looking for a social outlet, ask your social worker or in-centre dialysis nurse if your centre offers any organised events.
Play some music: This is one of the most effective methods for unwinding during your treatment. In fact, research found that dialysis patients who listened to music experienced less pain and nausea than those who did not.
Write about your experience in a blog, a notebook, or a tweet: Writing can help you work through your emotions and provide you the opportunity to share your experiences with friends, family, or even new dialysis patients.
Mentor new dialysis patients: It can be really rewarding to assist someone who is new to dialysis therapy. Inquire with your social worker about volunteering at the centre or starting a mentoring programme.
Discover something new: Is there something you've always wanted to learn more about but never had the time? Dive right in. Take an online class, read a book, listen to a podcast, view a video, or take a podcast.
Be an expert on kidneys: Continue to learn everything you can about treatment choices. Remember that some people change the type of dialysis they use at some point, so knowing as much as possible is beneficial.
Going through an illness can be difficult and can have a negative impact on one's mental health, so one should always try to nourish their inner peace and do things that make them happy and satisfied. Positivity and mental strength are the best ways to get through any illness, and one should never give up hope.
Protocols of dialysis:
Dialysis is based on the ultrafiltration of fluid across a semipermeable membrane, as well as the concept of solute dissipation. Diffusion is a property of materials in water that causes them to move in the opposite direction of a concentration gradient.
Dialysate or separate dialysis fluids flow on one flank of the semipermeable screen, while blood flows on the other. A selectively permeable layer is a thin material membrane with pores or holes of various sizes.
Minor solutes and fluids pass through the layer, but larger substances are blocked by the membrane (large proteins, red blood cells). When blood flows into the kidneys, the larger compounds are separated from the minor ones in the glomerulus, simulating the filtering process that occurs in the kidneys.
On the other hand, dialysis should not be viewed as a permanent solution; rather, it should be viewed as a temporary substitute for the kidney's function until the kidney can repair itself. On the other hand, chronic renal damage seldom heals on its own, necessitating a kidney transplant. Patients who have a kidney transplant have a higher life expectancy than those who receive dialysis.
Types of dialysis:
There are two major types of dialysis:
- Peritoneal Dialysis
- Hemodialysis
Hemodialysis
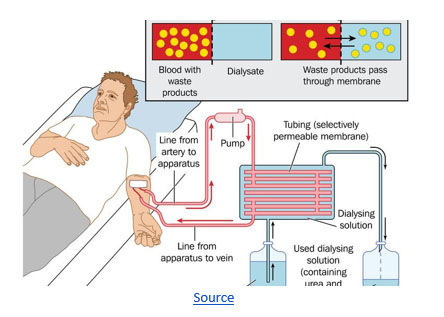
How does Hemodialysis work?
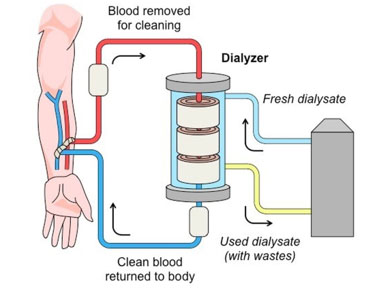
Your blood is pumped through tubes from your body into a dialysis machine during Hemodialysis. While in the machine, your blood passes through a dialyzer, which cleans your blood by filtering out some of the waste and surplus fluid. The cleaned blood is returned to your body via tubes from the dialysis machine.
Your doctor will need to make an access, or entry, into your blood vessels to get your blood into the dialyzer. This is referred to as vascular access.
Hemodialysis can be done at home, in a dialysis clinic, or by skilled medical personnel in a hospital.
Doctors will do the following during the procedure:
- A unique type of access termed an arteriovenous (AV) fistula is surgically implanted in your arm. They will have to connect an artery and a vein. (An external, central intravenous (IV) catheter may also be implanted for long-term dialysis, but this is less common).
- A huge Hemodialysis machine will be connected to you by the doctor.
- The machine draws blood, washes it in a particular dialysate solution to remove waste and moisture, and then reintroduces it into your body.
Recommendations for Hemodialysis:
- Hemodialysis is a four- to five-hour procedure frequently done multiple times a week. Because hemodialysis takes so long, it's a good idea to bring some reading material to pass the time while you're waiting.
- You can read, write, sleep, speak, or watch TV during Hemodialysis therapy.
- Hemodialysis is performed at home with the assistance of a partner, usually a family member or friend. You and your companion will undergo specific training if you opt to do home hemodialysis.
Hemodialysis: Risks and Benefits.
Muscle cramps and hypotension are two possible hemodialysis side effects (sudden drop in blood pressure). You may feel dizzy, weak, or sick to your stomach if you have hypotension. By eating healthy and taking your meds, you may avoid adverse effects.
A nutritionist will work with you to create a food plan that follows your doctor's instructions. Generally:
- You can consume beef and chicken, which are strong in protein (animal proteins).
- Different potassium limitations may apply to you.
- You may have to cut back on the amount of alcohol you consume.
- You may have to stay away from salt.
- Mineral phosphorus-containing foods may need to be limited (milk, cheese, nuts, dried beans, and soft drinks).
Dialysis is a mentally demanding process for a kidney patient, and being kind and sympathetic will help them get through this difficult period.






