
07
Apr
Gallbladder and Kidney Stone- Symptoms and Treatment
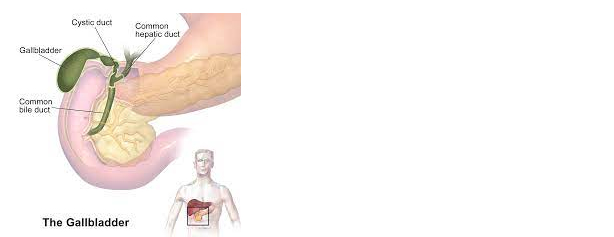
The gallbladder is an oval-shaped digestive organ situated on the right side of the abdomen, in front of the duodenum, and just below the liver. Its main function is to stock bile- a digestive fluid that subsequently enters the small intestine. The bile helps the digestive mechanism to carry away waste and break down fats into energy.
Source
Gallstones or gallbladder stones are sometimes formed due to hardened deposits of fluids in the gallbladder. It can also be caused by cholesterol piling up or a high accumulation of bilirubin in bile. The gallbladder stones can be found in varying sizes that might become as big as a golf ball if not treated in time.
Bile becomes concentrated if the gallbladder is not disposing of it completely or as frequently as it should. There is every chance of gallbladder stones forming over time in such a case. Other attributes are liver cirrhosis, sudden and quick weight loss, or even pregnancy.
What are the signs and symptoms of gallbladder stones?
Gallbladder stones don't show any signs or symptoms until the gallstones obstruct the bile ducts or until the hard deposits in the gallbladder reach a certain stage. Also, there are two types of gallstones, namely,

Source
Gallstones or gallbladder stones are sometimes formed due to hardened deposits of fluids in the gallbladder. It can also be caused by cholesterol piling up or a high accumulation of bilirubin in bile. The gallbladder stones can be found in varying sizes that might become as big as a golf ball if not treated in time.
Bile becomes concentrated if the gallbladder is not disposing of it completely or as frequently as it should. There is every chance of gallbladder stones forming over time in such a case. Other attributes are liver cirrhosis, sudden and quick weight loss, or even pregnancy.
What are the signs and symptoms of gallbladder stones?
Gallbladder stones don't show any signs or symptoms until the gallstones obstruct the bile ducts or until the hard deposits in the gallbladder reach a certain stage. Also, there are two types of gallstones, namely,
- Cholesterol gallstones: The most common type in India- it is the result of the accumulation of undissolved cholesterol and is yellow in colour.
- Pigment gallstones: These are generally formed when there is an excessive deposit of bilirubin in the bile duct.
To diagnose gallbladder stones, you can get some of the following reliable tests:
- CT scan and a detailed X-ray image of the gallbladder to assess the condition
- Ultrasound scan to check if there’s any inflammatory condition resulting in gallstones
- CMP (Complete Metabolic Panel) tests to find out if there's an increase in the bilirubin levels for an obstructive bile duct
- Liver enzyme test (part of blood test) results may be elevated when there's severe inflammation in the gallbladder, indicating a chance of gallstones
Symptoms of gallbladder stones
- Excessive pain in the right shoulder along with back pain
- Sudden and severe pain in the upper right portion of the abdomen area
- Indigestion, nausea and vomiting
- Cramping and discomfort because of gallstones
- Jaundice
Treatments surgical intervention-Laparoscopy
The most common treatment for gallbladder stones is called Cholecystectomy- the removal of the gallbladder through laparoscopy. This laparoscopic surgery is a minimally invasive surgery with a very small incision. It is a painless procedure, and the patient can go about their day normally within a week.
Today, one of the most common surgeries performed worldwide to remove gallbladder stones is Cholecystectomy. If gallbladder stones are neglected, and treatment is not taken on time, one might be exposed to the dangers of slipping into dangerous conditions like cholecystitis and sepsis or gallbladder cancer in the future.
About kidney stones
Source
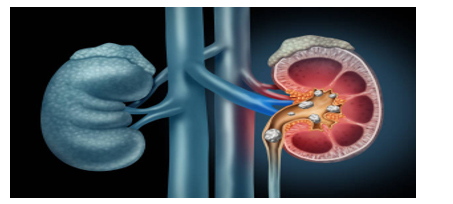
Kidneys, located on both sides of the spine, are bean-shaped and are one of the most important organs in the human body. They are roughly around 5 inches long. The kidneys' primary function is to purify and filter the blood by clearing wastes, maintaining the body's fluid balance, and sustaining the right levels of electrolysis. Blood circulation in the body passes through the kidneys around 40 times a day.
Kidney stones which in medical terms are called Nephrolithiasis are a gathering of small hard deposits. They are the acidic salts and hard deposits of minerals that bind together in concentrated urine. Although they don't cause any permanent damage to the kidneys if treated in time, they can cause a lot of pain while passing through the urinary tract.
What are the main types and symptoms of kidney stones?
There are four main types of kidney stones which include
- Uric acid: This is one of the common types of kidney stone and is more prone to people who are diabetic, obese, have high blood pressure, and relatively low HDL levels (good cholesterol). When urine has high acidic levels, it can lead to kidney stones. Purine-rich diets ( mainly animal proteins, shellfish and meats) can increase acidic levels in urine.
- Calcium oxalate: Insufficient calcium consumption and less fluid intake are common contributing factors to kidney stones.
- Struvite: This type of stone formation is found mainly in those who are affected by urinary tract infections.
- Cystine: Cystinuria is a genetic disorder mainly inherited from the parents where cystine (a naturally occurring acid in the body) tends to leak from the kidney to the uterine.
Major symptoms of kidney stones:
- Extreme and severe pain on either side of the lower back
- Excessive pain while passing urine
- Frequent urination sensation
- Blood mixup in urine
- Nausea and vomiting
- Sometimes sweating
Diagnosis of kidney stones:
- Blood tests and urine tests are done to determine the health of the kidneys
- High-resolution CT scan
- KUB X-ray (kidney-ureter-bladder X-ray) where the exact size and position of the stone is determined for treatment
- IVP (intravenous pyelogram) is a special type of X-ray of the urinary network taken after injecting a dye.
- Stone analysis tests are done once the kidney stone comes out of the urine to find out the type of stone to prevent it in the future
Treatment for kidney stones:
- For small hard deposits of stones, patients are advised to drink lots of water and administer IV fluids so that the stones dissolve and pass away through urine without the need for surgery.
- Another form of treatment is shock-wave laser lithotripsy, which is a non-invasive procedure that uses high energy sound waves to break the stones into smaller fragments and will pass out easily through urine
- Another type of treatment is ureteroscopy, where an endoscope is inserted through the ureter to destroy the cluster of particles
- In rare cases, percutaneous nephrolithotomy/ nephrolithotripsy procedure is done to flush out the segregation of stones.
For the majority of the people affected with kidney stone formations, there's a high chance of recurrence. The stone analysis test should be done post-treatment to determine the root cause of the stone formation. Balanced food intake, consuming enough fluids and reducing excess salt intake will help reduce the risk of stone formation.






